As an affiliate I earn from qualifying purchases.

It’s important to understand the science behind skincare products, so you’re taking care of your skin the right way. There’s a lot of different reasons why weather can impact your skin’s health and appearance. For example, when it gets colder your skin can become dry, flaky, and irritated. It’s important to always adjust your skincare routine to help your face stay hydrated.
I’ll go into how our skin’s microbiome changes with the seasons, and the impact of UV radiation. I’ll also provide tips and recommendations for adjusting your skincare routine to your skin’s needs. If you understand the science of skincare, then you can keep your skin healthy for the rest of the year. It’s important to know the scientific factors, so you can learn about your skin’s microbiome and the damaging effects of UV radiation.
1. Dry Air = Dry Skin
Drier air can really increase moisture loss from the skin because of several scientific factors, so let’s talk about why this happens:
Relative Humidity:
The moisture content in the air is measured as relative humidity (RH), which represents the percentage of water vapor in the air compared to the maximum amount the air can hold at a specific temperature. When the air is dry, it has a lower RH, meaning it contains less moisture.
Osmosis and Water Movement:
Skin cells, like all living cells, have a semi-permeable membrane. This means they allow the passage of water molecules in and out of the cell. The movement of water across this membrane is a process called osmosis. Water naturally moves from areas of higher water concentration (inside the skin cells) to areas of lower water concentration (the drier air) to equalize the concentrations.
Transepidermal Water Loss (TEWL):
If you watch Dr. Dray on YouTube, then you know what I’m talking about. The skin has a protective layer called the stratum corneum, which is made of dead skin cells and lipids (fats). This layer acts as a barrier to stop your body from losing water. However, in dry conditions the stratum corneum can become less strong. The dry air draws moisture from the skin, leading to an increase in transepidermal water loss (TEWL).
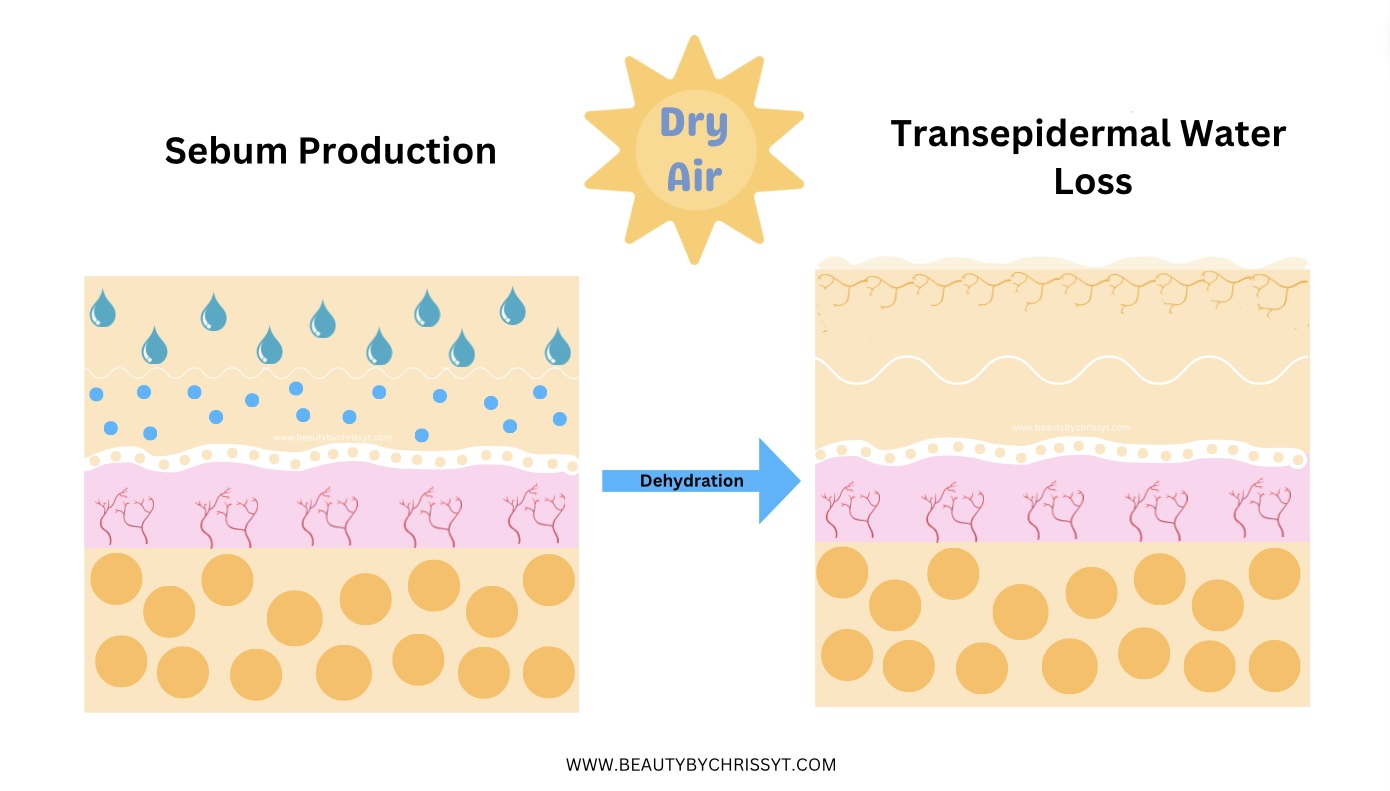
Natural Moisture Evaporation:
Your skin naturally releases moisture through a process called insensible water loss, even if you’re not sweating. This moisture loss is caused when the surrounding air is dry. The dry air absorbs the moisture from your skin more easily, causing your skin to become dry.
Sebum Production:
Your skin produces a natural oil called sebum, which helps keep the skin moisturized. In drier weather, the sebaceous glands will produce less sebum, making it harder to keep your skin hydrated.
Sensory Perception:
Dry air can also affect your perception of skin dryness. It can make your skin feel drier and more uncomfortable, even if your dry skin isn’t bad. This can make you itchy or rub your skin, which can break the skin’s barrier and create micro tears.
Basically, drier air has lower relative humidity, and this difference in moisture concentration between the air and your skin leads to increased moisture loss through osmosis and evaporation.
2. Decreased UV Exposure Requires Adjustments
Vitamin D Production:
UV radiation from the sun is how we get vitamin D in our bodies. When our skin is exposed to UVB rays it synthesizes vitamin D, which is important for different reasons -including bone health, immune system support, and healthy skin.
Melanin Production:
UV exposure triggers the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. This gives some level of protection against the harmful effects of UV radiation by absorbing and dispersing UV rays. But your UV exposure can slow down melanin production, leaving your skin more vulnerable to UV damage when you’re in the sun.
Skin Texture and Tone:
Long exposure to the sun like tanning, or not using any type of sunscreen can cause a lot of skin issues like sunburn, premature aging, and hyperpigmentation (dark spots). The less time you spend in the sun, it gives your skin more time to recover and repair these effects. This means changing your skincare routine during the winter can improve your skin texture and even out your skin tone.
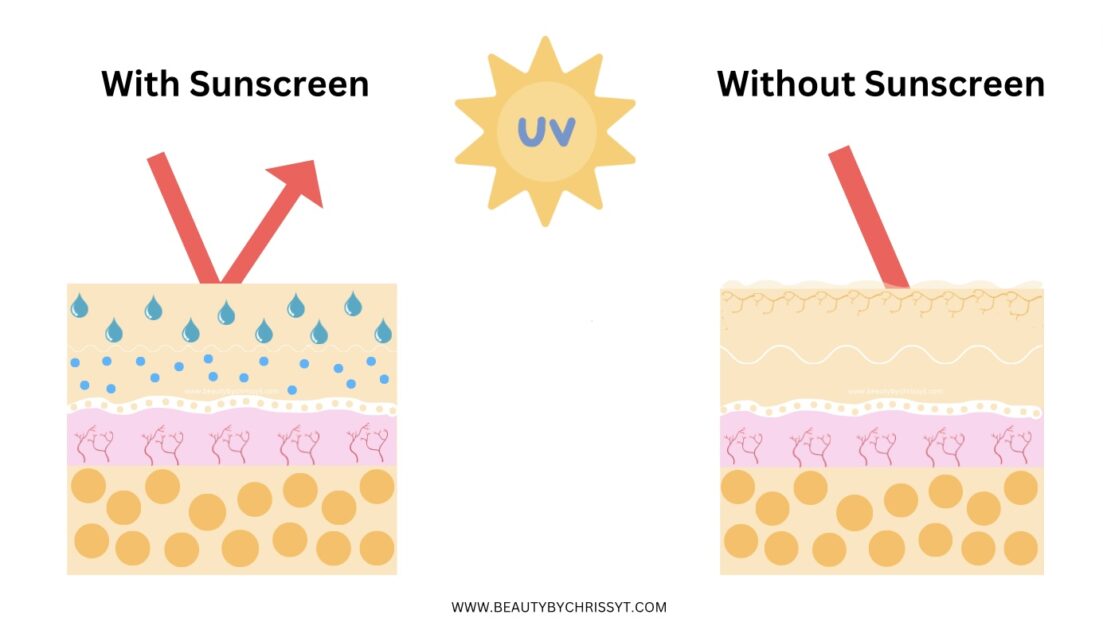
Reduced Risk of Skin Cancer:
Less time in the sun lowers the risk of skin cancer, since UV radiation is a known carcinogen. However, it’s important to know that even if you’re not in the sun a lot, you can still get exposed anytime you’re outside. Don’t let the lack of sun fool you, so keep your sun habits all year, and make sure you’re ALWAYS using sunscreen.
Skin Sensitivity:
UV radiation can make the skin more sensitive and irritated, but the less time you’re in the sun can help these sensitive skin conditions. That means your skincare routine should include gentler products for your skin.
3. Exfoliation Is Key For Renewal
Exfoliation is a big step in your skincare routine, because it plays an important role for skin by removing dead skin cells from the surface. This process is important for several reasons:
Cell Turnover:
The skin is constantly renewing itself through a process called cell turnover. New skin cells are generated in the lower layers of the epidermis and gradually move up to the surface. As they reach the surface, they become flattened and filled with keratin, a tough protein. Eventually, these cells become dead and are shed from the skin. Exfoliation helps this shedding process because newer, healthier cells replace the old ones.
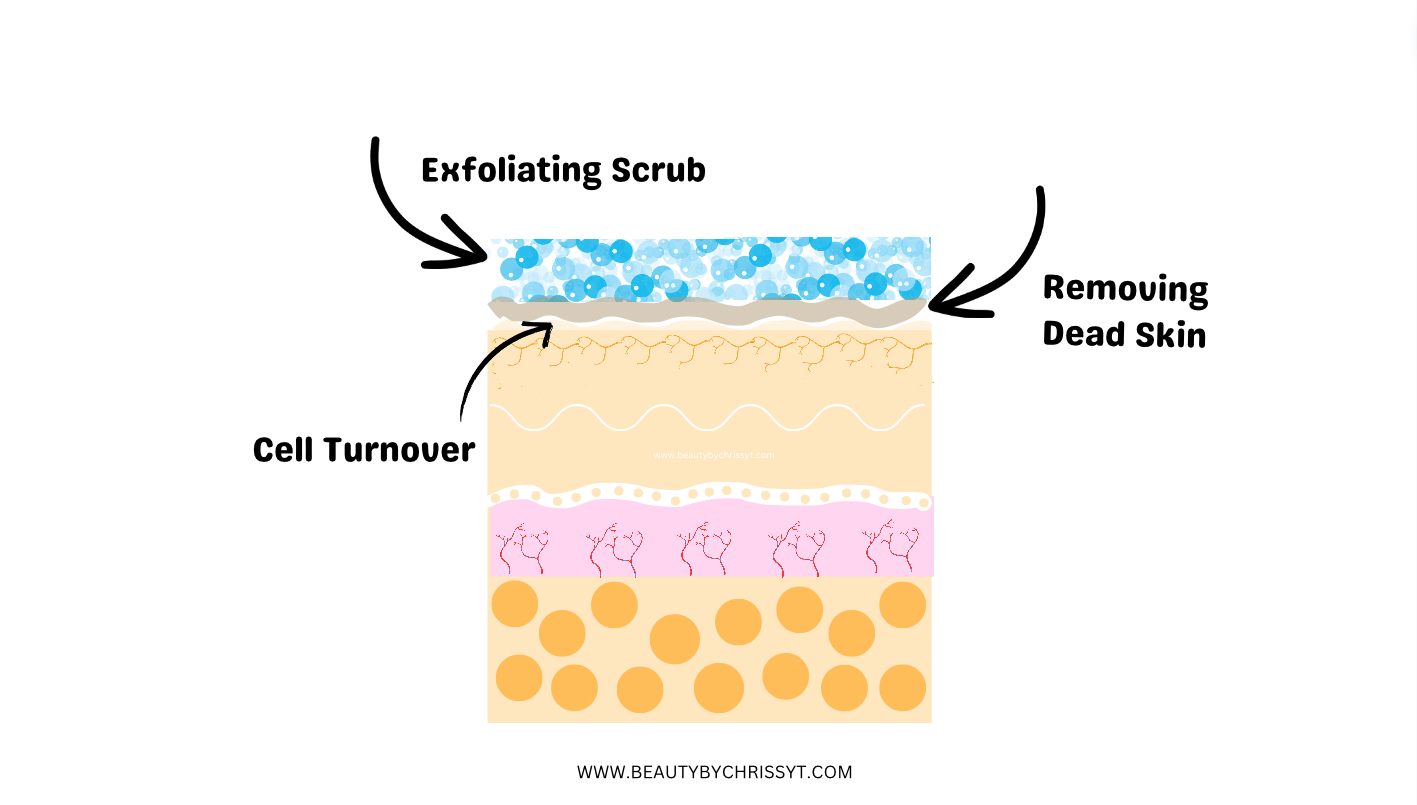
Improved Skin Texture:
Exfoliation helps to smooth skin by getting rid of rough, uneven surfaces. By removing dead cells and encouraging new younger cells, exfoliation can cause a smoother and more even skin texture.
Brighter Complexion:
Dead skin cells can make the skin look dull and tired. Exfoliating regularly can help brighten your skin, giving you a healthy glow.
Unclogging Pores:
Exfoliation can help prevent and remove clogged pores. When dead skin cells pile on the skin’s surface, they can mix with sebum (skin oil) and other debris, leading to blackheads and whiteheads. By removing these dead cells, exfoliation can keep pores clear and reduce breakouts.
Enhanced Product Absorption:
Exfoliated skin is better prepared to absorb skincare products, like moisturizers and serums. Without the barrier of dead cells, these products can penetrate into the skin, making them more effective.
Minimized Signs of Aging:
Regular exfoliation can reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. It encourages collagen production and helps keep your skin’s elasticity, so you‘ll yonger.
Treatment of Skin Concerns:
Exfoliation can be for specific skin concerns. For example, chemical exfoliants like alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) and beta hydroxy acids (BHAs) help with hyperpigmentation, acne, and uneven skin tone. But it’s better to exfoliate a few times a week rather than everyday, because it can cause micro tears and do more harm than good. Choose the right exfoliant for your skin type, so you’re not using something too harsh. At the same time, you don’t want something that doesn’t remove dead cells either. Read the ingredients, and feel the texture of the exfoliator before making a decision. You don’t want to waste money on a product that your skin doesn’t like.
Exfoliating too much can cause skin irritation, dryness, and sensitivity. How much you of exfoliate should be up to on your skin’s needs. Also, it’s very important to use sunscreen everyday (even if you don’t exfoliate) since your skin can get UV damage.
Conclusion
Understanding the science behind your skin can help you create a skincare routine made for you depending on what your skin needs in colder weather. If you focus on hydration, protection, and what you need for different environments, then you can maintain healthy skin. Changes in temperature and humidity can cause your skin to get dry, dull, and easily damaged. Understanding the science of your skin can help you create a skincare routine that specifically caters to what your skin needs this time of year.
Amazon and the Amazon logo are trademarks of Amazon.com, Inc, or its affiliates.



